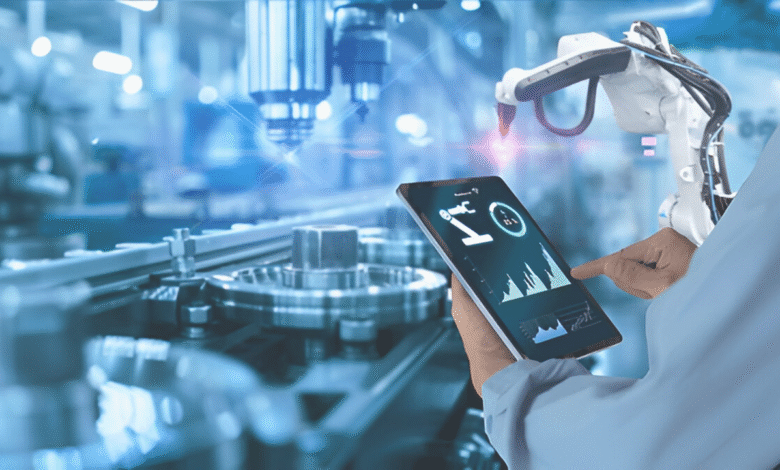

The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is rapidly transforming Pakistan’s manufacturing landscape, ushering in a new era of smart factories and data-driven production. As industries worldwide embrace digitalization, Pakistani manufacturers are increasingly adopting IIoT solutions to enhance efficiency, reduce operational costs, and improve product quality. From textile mills to automotive plants, the integration of connected sensors, automation, and real-time analytics is revolutionizing traditional processes. This technological shift is not just a trend but a necessity for Pakistan to remain competitive in the global market, making IIoT a cornerstone of the country’s industrial future.
Pakistan’s manufacturing sector, long reliant on conventional methods, is now at a critical juncture where embracing Industrial IoT (IIoT) could determine its growth trajectory. With challenges such as energy shortages, high production costs, and global competition, IIoT offers solutions through predictive maintenance, energy optimization, and streamlined supply chains. Government initiatives like the Digital Pakistan Vision and increasing private-sector investments in smart technologies are accelerating this transition. As more industries recognize the potential of IIoT, Pakistan stands on the brink of an industrial revolution that could redefine productivity, sustainability, and economic resilience in the years to come.
The Rise of Industrial IoT in Pakistan’s Manufacturing Sector
The Current State of Pakistan’s Manufacturing Sector
Pakistan’s manufacturing sector has long been a cornerstone of its economy, contributing significantly to GDP and employment. Traditional industries such as textiles, cement, and steel dominate, but there is a growing shift toward modernization. With increasing global competition, manufacturers are under pressure to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance product quality. This has led to a rising interest in Industrial IoT (IIoT), which offers data-driven insights and automation to streamline operations.
Key Drivers of IIoT Adoption in Pakistan
Cost Efficiency and Productivity Gains
IIoT enables predictive maintenance, reducing unexpected machine failures and downtime. Sensors monitor equipment health in real-time, allowing timely interventions that save costs.
Global Competitiveness
To compete internationally, Pakistani manufacturers must adopt advanced technologies. IIoT helps improve product quality and supply chain transparency, making exports more competitive.
Energy Optimization
With frequent energy shortages, IIoT helps optimize power consumption through smart grids and automated energy management systems.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Real-time analytics provide actionable insights, helping manufacturers optimize workflows and reduce waste.
Applications of IIoT in Pakistani Industries
Smart Textile Manufacturing
Pakistan’s textile industry, a major export earner, is leveraging IIoT for automated looms, quality control, and inventory management. Smart sensors detect fabric defects early, reducing waste and improving efficiency.
Automotive and Assembly Lines
Automotive manufacturers use IIoT for robotic automation, real-time tracking of assembly lines, and predictive maintenance, ensuring smoother production cycles.
Pharmaceutical and Quality Assurance
IIoT ensures compliance with strict regulatory standards by monitoring temperature, humidity, and production conditions in real-time, reducing errors in drug manufacturing.
Energy and Utilities Management
Factories integrate IIoT-based energy monitoring systems to cut costs and reduce reliance on unstable power supplies.
Challenges in IIoT Implementation
High Initial Investment Costs
One of the most significant barriers to Industrial IoT (IIoT) adoption in Pakistan is the substantial upfront capital required. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), which form the backbone of the manufacturing sector, often lack the financial resources to invest in advanced sensors, automation systems, and cloud-based analytics platforms. The cost of retrofitting legacy machinery with IoT-enabled devices, along with expenses for software integration and cybersecurity measures, makes implementation prohibitively expensive for many businesses. Without accessible financing options or government subsidies, widespread adoption remains a challenge.
Lack of Skilled Workforce and Technical Expertise
The successful deployment of IIoT demands a workforce proficient in data analytics, machine learning, and industrial automation. Unfortunately, Pakistan faces a severe shortage of professionals trained in these cutting-edge technologies. While some universities and technical institutes have begun offering IoT-related courses, the pace of skill development lags behind industry needs. Additionally, many existing factory workers lack digital literacy, making it difficult to transition from manual processes to smart manufacturing systems.
Unreliable Internet Connectivity and Infrastructure
IIoT relies heavily on seamless data transmission between devices, machines, and cloud platforms. However, inconsistent internet connectivity especially in industrial zones outside major cities poses a major hurdle. Frequent power outages and slow network speeds disrupt real-time monitoring and analytics, reducing the efficiency of IoT systems. Furthermore, Pakistan’s limited 5G rollout and underdeveloped IT infrastructure hinder the full potential of IIoT, making it difficult for manufacturers to implement high-bandwidth applications like Augmented reality (AR) for maintenance or AI-driven quality control.
Cybersecurity Risks and Data Privacy Concerns
As factories become more interconnected, they also become vulnerable to cyber threats such as hacking, data breaches, and ransomware attacks. Many Pakistani manufacturers lack robust cybersecurity frameworks, exposing sensitive production data and operational systems to potential exploitation. The absence of standardized data protection regulations further complicates the issue, as companies struggle to ensure compliance with international security norms.
The Future of IIoT in Pakistan
Government-Led Digitalization Initiatives
Pakistan’s future Industrial IoT (IIoT) adoption will be significantly influenced by government policies like the Digital Pakistan Vision and Smart Industry 4.0 frameworks. Expect increased public-private partnerships, tax incentives for tech adoption, and grants for SMEs to implement IIoT solutions. The establishment of special economic zones with integrated smart infrastructure could accelerate this transformation.
Expansion of 5G and Edge Computing Networks
The rollout of 5G technology and edge computing infrastructure will remove current bandwidth limitations, enabling real-time data processing for mission-critical IIoT applications. This will particularly benefit distributed manufacturing systems, autonomous robotics, and augmented reality-based maintenance operations across Pakistani factories.
Emergence of Local IIoT Solution Providers
A growing ecosystem of Pakistani tech startups and software houses will develop localized IIoT platforms tailored to domestic manufacturing needs. These cost-effective, vernacular-supported solutions will drive wider adoption among SMEs while reducing dependence on expensive foreign systems.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Advanced predictive analytics powered by AI will transform IIoT deployments from basic monitoring to prescriptive maintenance and autonomous decision-making. Pakistani manufacturers will increasingly use these tools for quality control, supply chain optimization, and energy management.
Workforce Upskilling and Educational Reforms
Technical universities and vocational institutes will introduce specialized IIoT certification programs to address the skills gap. Industry-academia collaborations will produce a new generation of engineers proficient in cyber-physical systems, data science, and industrial automation.
Sustainable Manufacturing Through IIoT
Energy-intensive industries will leverage Industrial IoT for green manufacturing initiatives, using smart sensors to optimize resource consumption and reduce carbon footprints. This aligns with global sustainability trends and improves export competitiveness.
Cybersecurity and Regulatory Frameworks
As adoption grows, Pakistan will develop standardized IIoT security protocols and data governance policies. Expect mandatory cybersecurity certifications for industrial equipment and blockchain-based solutions for secure supply chain transactions.
Cross-Industry IIoT Convergence
The boundaries between manufacturing, agriculture, and logistics will blur as Industrial IoT creates interconnected ecosystems. For instance, textile factories will integrate with smart cotton farms and automated logistics providers for end-to-end visibility.
Global Competitiveness and Export Growth
Early Industrial IoT adopters in Pakistan’s automotive, pharmaceutical, and textile sectors will gain significant quality and efficiency advantages, helping them penetrate premium international markets and attract foreign direct investment.
Read More: Digital Pakistan & Freelancing: Opportunities for the Youth
Conclusion
The Industrial IoT is poised to revolutionize Pakistan’s manufacturing sector, offering unprecedented opportunities for growth, efficiency, and global competitiveness. By integrating smart sensors, automation, and data analytics, Pakistani industries can optimize production processes, reduce downtime, and enhance product quality. While challenges such as high implementation costs and a skills gap persist, strategic investments in digital infrastructure and workforce training can pave the way for widespread IIoT adoption. As more manufacturers embrace this transformation, Pakistan’s industrial landscape is set to become more resilient, innovative, and aligned with global Industry 4.0 standards.
Looking ahead, the success of Industrial IoT (IIoT) in Pakistan will depend on collaborative efforts between the government, private sector, and educational institutions. Policymakers must incentivize technology adoption, while industries should prioritize cybersecurity and continuous upskilling of their workforce. With the right framework in place, IIoT can drive sustainable industrial growth, attract foreign investment, and position Pakistan as a key player in smart manufacturing. The journey toward a fully connected industrial ecosystem may be gradual, but the potential rewards increased productivity, reduced costs, and enhanced global trade make it a transformative leap worth taking.
FAQs
What is Industrial IoT (IIoT)?
Industrial IoT refers to interconnected sensors and devices in industrial settings that collect and analyze data to optimize manufacturing processes.
How is IIoT benefiting Pakistan’s textile industry?
IIoT improves fabric quality control, reduces waste, and automates production, enhancing efficiency in textile manufacturing.
What are the main challenges of Industrial IoT in Pakistan?
High implementation costs, cybersecurity risks, and a lack of skilled professionals are key challenges.
How does Industrial IoT help in energy management?
Smart sensors monitor and optimize energy usage, reducing costs and reliance on unstable power supplies.
What is the future of Industrial IoT in Pakistan?
With advancements in 5G, AI, and government support, IIoT adoption is expected to grow, revolutionizing Pakistan’s industrial sector.











2 Comments